MaksutovDmytro
April 23, 1896, Odesa, Russian Empire (today Ukraine) —
August 12, 1964, Leningrad, USSR (today Saint Petersburg, Russia)
Meniscus telescope
Aberration. A horrible word, especially for astronomers. It means that the telescope transmits distorted or blurred images of space objects.

First refracting telescopes appeared consisting of two lenses, the objective and the eyepiece. Galileo Galilei used this telescope to watch the sky. Chromatic aberration was their weak point. The images were blurry and had colored stripes and spots. For example, the Moon had a reddish edge on one side and a bluish-red edge on the other.
Then reflecting telescopes were designed which were composed of two mirrors and one lens. Their author is considered to be Isaac Newton. Chromatic aberration was corrected, but spherical aberration appeared instead. As a result, the images were not clear enough. Hubble was keeping sending blurred images until a team of astronauts went into orbit and repaired the telescope.
In order for astronomers to get a better look at our own and other galaxies, optical engineers have been experimenting with the shape, distance, and positions of lenses and mirrors for more than 400 years. And sometimes they created completely new types of telescopes, as Ukrainian spacing of lenses did.
In 1941, it was revealed that the German Army was going to capture Leningrad. Maksutov and other scientists who were then working at the State Optical Institute were hastily evacuated to Yoshkar-Ola. The idea of a new telescope design came to him right on the train. Later, the scientist said that there was simply nothing to do there but think. Maksutov took a reflecting telescope as a basis and, to get rid of spherical aberration, changed the trajectory of the rays, placing a meniscus (a lens similar in shape to a bowl) in their path. Within a few months, Maksutov completed all the calculations and even tested the first meniscus telescope assembled by local craftsmen.
After the end of the war, thousands of meniscus telescopes appeared in schools, and several more powerful ones went to observatories in Kazakhstan, Georgia, Crimea, etc. One was even installed on Cerro El Roble mountain in Chile in
However, the most famous discovery with the Maksutov telescope was made at the observatory in Almaty. In 1969, two Ukrainian astronomers Klym Churyumov and Svitlana Gerasimenko, came there to observe comets. While “hunting” for Comas Solà comet Gerasimenko made a few pictures. Looking at them, Churyumov noticed an object that resembled an undiscovered comet. He analyzed everything carefully again, and yes, his assumption was correct. The comet was named 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, it is often called Churyumov comet. It would probably have remained unknown for the general public if an automatic interplanetary station Rosetta hadn’t explored it in 2004. It was one of the most challenging missions in the history of space exploration. The comet, which Churiumov saw in the images, resembled two molded lumps of clay, the larger one had a size of 4.1×3.2×1.3 km, and the smaller one was 2.5×2.5×2.0 km in size. It took Rosetta ten years to catch up with the comet, and seven hours to the Philae lander research vehicle land on its imperfect surface.
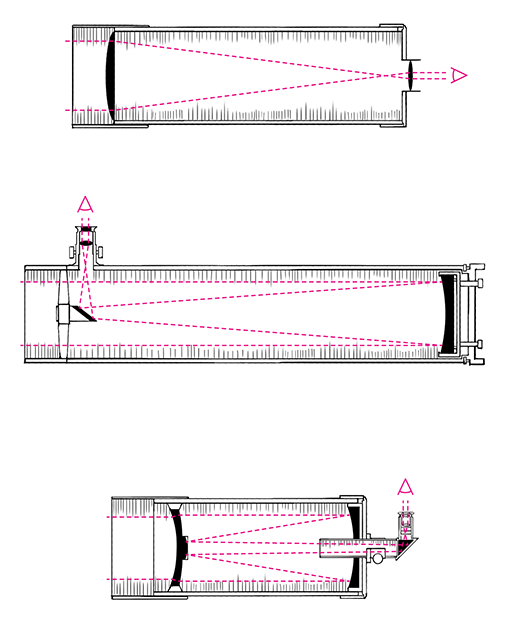
Refractor (upper), reflex and meniscus (lower) telescopes
It is generally believed that comets were formed in the young solar system from the same material as planets and natural satellites. Therefore, researching the comets we can learn more about those times. zzThat is why ten instruments were installed on board of Philae lander: from a drill for extracting rock samples to spectrometers and a device for measuring the ratio of stable isotopes particles. The mission ended in 2016, but scientists are still analyzing the results.
For the first time in history, a research vehicle landed on the surface of a comet discovered by two Ukrainians after seeing it through a telescope designed by another Ukrainian. It’s a beautiful story.